The Quick Fix is a Fake Fix
There is no real quick fix when it comes to health or mental health. Benzos may help in a crisis of unusual stress or anxiety. They work nearly immediately, unlike the slower arc of time that SSRIs need to fully kick in. While a fast-acting drug may seem like a perfect solution, overprescribing has developed into a dangerous trend. Medical school does not train general practitioners about proper guidelines for prescribing benzodiazepines, and in many cases, doctors are “winging it” with disastrous results for their patients.44 While quick action may serve a pressing need in a dire situation, benzodiazepines are not at all suitable for long-term use. Coupled with the lack of education, and time pressures that doctors face, there has developed a tendency toward giving patients a quick answer to everything that is troubling, without taking time to search for more underlying reasons for anxiety or insomnia, or other conditions. This tendency has led to at least a doubling of the number of benzo prescriptions over the last few years.3
 A good gardener knows there is no such thing as a quick fix. A good mechanic also knows. It takes getting into the guts of the situation and digging around and testing to discover the actual problem. Then you can implement a real resolution to the root cause of the problem. That is our prime goal at Alternative to Meds Center. We take the time necessary to do the work.
A good gardener knows there is no such thing as a quick fix. A good mechanic also knows. It takes getting into the guts of the situation and digging around and testing to discover the actual problem. Then you can implement a real resolution to the root cause of the problem. That is our prime goal at Alternative to Meds Center. We take the time necessary to do the work.
Using an arsenal of diagnostic tools such as testing for deficiencies or the presence of toxins in the body, and even testing genetic factors that can be relevant, we focus on resolving the causes of symptoms that likely lead to seeking a prescription of benzodiazepines in the first place. Non-physical contributory factors are also explored in counseling and life coaching and other therapies for authentic relief. Drugs can only mask symptoms, numb unwanted feelings, and make a person less aware of their very real pain or discomfort. Sometimes, indeed, this is a necessary and even humane action. However, they do nothing to cure or resolve the source of the problem. At Alternative to Meds Center, we aim to do just that; find the root cause(s), and address those for lasting relief. That way, coming off benzodiazepines will not leave a person in dire straits. This is because their symptoms will be reduced markedly. Reduction of symptoms is typical even during the pre-withdrawal phase of our program.
Benzodiazepines are primarily used for lessening anxiety and promoting sleep. The most recent advisories both in the US and abroad recommend short-term use only, no longer than a number of weeks.12 Benzodiazepines are the most common category of prescription medications that Alternative to Meds Center addresses. An unsupported benzodiazepine withdrawal process could be considered by many, to be close to impossible.1,2,7,10-12
These are powerful drugs and can alter neurochemistry even after short-term use, (4 weeks or less), and especially when used long-term (more than 4 weeks) may end up causing more adverse reactions than they were targeted to address.40 Never abruptly stop taking benzodiazepine drugs, as to do so may intensify and lengthen the withdrawal symptoms considerably. Alternative to Meds Center specializes in relieving benzodiazepine discontinuation syndrome and the protracted symptoms of withdrawal that individuals who taper at home may unfortunately face. At the center, we focus on correcting the causes of anxiety or insomnia so that an individual can be free of these symptoms, and also free of benzodiazepine adverse effects, and free from benzodiazepine withdrawals.
Learn About the Alternatives to Benzodiazepines
We have found that in many cases of chronic anxiety, the individual has in fact accumulated neurotoxins and heavy metals in the body, which can overstimulate the CNS. A clear association has been reported in various studies observing the effects of toxic exposures to pesticides, heavy metals, and other neurotoxic materials. According to research, humans, as well as animals and aquatic creatures, are susceptible to the overstimulating effects of such exposures. In fact, this overstimulation could well have been the reason for the prescription of benzodiazepine medication in the first place.18-24
Clearly, a person who experiences constant anxiety may suffer from a burden of neurotoxic accumulations, such as mercury, lead, chemical food additives, aspartame, industrial cleaners, and pesticides. For long-term relief and neurotransmitter rehabilitation, the toxic burden has to be removed.
Can Pesticides Create Anxiety?
Consider how pesticides kill their prey. A grasshopper may encounter a toxic insecticide that is specifically designed to kill it. The following summarizes how the process works:
- The toxin gets absorbed through the grasshopper’s exoskeleton.
- The toxin moves through the body and enters the nervous system.
- The poison (pesticide) molecules cause the acetylcholine channels of the grasshopper’s nervous system to lock in the “open” position. These channels cannot now close.
- Because acetylcholine is a neurochemical with stimulant or excitatory properties, this will cause the grasshopper to jump, twitch, or convulse.
- The continued influx of acetylcholine causes catatonia (repetitive motions) to the point of exhaustion and a comatose state.
- The grasshopper eventually dies.
 Humans and grasshoppers as well as many other life forms have some similar neurology.13,14 They also share reactions to toxins that have invaded the CNS. If the toxic load in a person is potent enough, the excitatory effects of the toxic material can cause similarly unbridled overstimulation, which we may recognize as chronic anxiety. Studies have shown the toxic effects on neurons by exposure to metal nanoparticles as an example.4
Humans and grasshoppers as well as many other life forms have some similar neurology.13,14 They also share reactions to toxins that have invaded the CNS. If the toxic load in a person is potent enough, the excitatory effects of the toxic material can cause similarly unbridled overstimulation, which we may recognize as chronic anxiety. Studies have shown the toxic effects on neurons by exposure to metal nanoparticles as an example.4
Individuals who have been exposed to environmental poisoning have developed certain immunological syndromes and neurological conditions as a result.15
Similar to the grasshopper, an over-accumulation of acetylcholine in humans can cause neurochemical overstimulation. Our nervous systems use acetylcholine for stimulation. We are subject to bioaccumulation and exposure to many types of toxins that can inflict this excitatory property and are also linked to a troubling number of other types of health breakdowns.
We are commonly exposed to neurotoxins:
- Mercury* from dental amalgams, lightbulbs, lead, and other heavy metals are neurotoxic. 15-17,31,41
- Aspartame is toxic to the myelin sheath and is a neuron disruptor.5
- MSG is toxic to brain cells.6
- Mycotoxins and microfungi can cause disease and death in humans.26,27
- Chemicals in cleaning products (phthalates and other endocrine disruptors) 9
- Chemicals such as phthalates, mercury, talc, etc., in personal products 25
- Chemicals in processed foods 28
- The “forever chemicals” (PFAS) are linked to immune and endocrine disruption, cancers, and other health issues.42,43
- Water treatment residues create cellular dysfunction including chlorine, fluoride, dioxins, and PCBs, for example. 29
- We advise researching all personal and household products for safety before use.
*According to a study by Ganser and Kirschner, mercury can damage the myelin sheath, a potentially life-saving discovery from their neurotoxicity research.
 Toxins can significantly impact endocrine glands and can cause hormone imbalance, such as adrenal burnout, and elevated cortisol levels.
Toxins can significantly impact endocrine glands and can cause hormone imbalance, such as adrenal burnout, and elevated cortisol levels.
Often, the source of anxiety is the build-up of neurotoxins over the lifetime of the person. This is because these toxins and heavy metals are fat-soluble, and they tend to accumulate and linger in fatty tissue over time and have properties that can overstimulate and induce other impairments within the central nervous system.5,31
These residual toxic effects will likely continue to negatively impact neurology until they can be removed. The good news is that these toxic elements can be removed safely, and health can be restored once again. It is possible to investigate, discover, and correct the varied root causes of anxiety. We also provide counseling that can help overcome anxiety and its negative impacts that may have affected a person on so many levels of their life.
The CDC reported in the 2020 toxicological profile for lead, that the neurological impacts of both short-term and chronic lead exposure in children and in adults are significant. The reported effects included cognitive impairments, intellectual deficits, delayed childhood developments, mood disruption, compromised immune system, depression, and a host of other reactions to lead exposure. 41
We have observed at Alternative to Meds that psychological therapies may be enhanced in their effectiveness after unburdening bioaccumulation of toxic materials.
How Does Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Affect the Body?
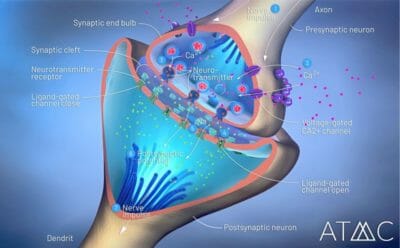 Clinicians and researchers continue to search for more clarity on why benzodiazepine withdrawal is so difficult. Coming off these drugs is disruptive to the entire CNS and affects the amazingly complex relationships between neural connections, glands, muscles, etc., throughout the entire body.
Clinicians and researchers continue to search for more clarity on why benzodiazepine withdrawal is so difficult. Coming off these drugs is disruptive to the entire CNS and affects the amazingly complex relationships between neural connections, glands, muscles, etc., throughout the entire body.
Generally, the medical consensus is that at least in part, benzodiazepines act on GABA in the body.30 GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the body’s primary inhibitory (calming, dampening) neurotransmitter. One of the effects of benzodiazepine drugs is to make nerve synapses in the brain more permeable to GABA. This means that GABA’s dampening effects are strengthened, and therefore more able to slow or inhibit more excitatory nerve impulses traveling along the CNS. Hence the sedating effect of benzo drugs. However, the presence of benzodiazepines causes the body to use up available GABA. When the GABA has been spent, the result is that everything can become overstimulating.9
Removal of Toxic Load Helps Restore Neurochemistry
GABA is available for purchase as a natural supplement. However, GABA and other natural neurochemicals can be rendered ineffective because of the presence of toxic elements that impair the CNS.31 Alternative to Meds Center programs are designed to remove this toxic load to enable the body to utilize natural substances like GABA, and others, to normalize neurochemistry. Restoring neurochemistry by cleaning out toxins typically decreases anxiety, mental fog, fatigue, and other symptoms. Testing helps confirm this significant marker, that informs us when we can begin to comfortably reduce anxiety medication. Given proper support, one does not have to decide between continuing medication or continuing symptoms.
 Pre-marketing drug trials are often short, and there is typically scant attention given to withdrawal symptoms, especially for novel drugs. There is every chance that withdrawal symptoms from certain drugs may extend beyond what has been described in the published medical literature. There is a voluntary reporting system that patients, doctors, and other care providers can use to forward information on withdrawals and other drug adverse events to drug regulators in the US. Please visit the
Pre-marketing drug trials are often short, and there is typically scant attention given to withdrawal symptoms, especially for novel drugs. There is every chance that withdrawal symptoms from certain drugs may extend beyond what has been described in the published medical literature. There is a voluntary reporting system that patients, doctors, and other care providers can use to forward information on withdrawals and other drug adverse events to drug regulators in the US. Please visit the 
 A good gardener knows there is no such thing as a quick fix. A good mechanic also knows. It takes getting into the guts of the situation and digging around and testing to discover the actual problem. Then you can implement a real resolution to the root cause of the problem. That is our prime goal at Alternative to Meds Center. We take the time necessary to do the work.
A good gardener knows there is no such thing as a quick fix. A good mechanic also knows. It takes getting into the guts of the situation and digging around and testing to discover the actual problem. Then you can implement a real resolution to the root cause of the problem. That is our prime goal at Alternative to Meds Center. We take the time necessary to do the work. Humans and grasshoppers as well as many other life forms have some similar neurology.13,14 They also share reactions to toxins that have invaded the CNS. If the toxic load in a person is potent enough, the excitatory effects of the toxic material can cause similarly unbridled overstimulation, which we may recognize as chronic anxiety. Studies have shown the toxic effects on neurons by exposure to metal nanoparticles as an example.4
Humans and grasshoppers as well as many other life forms have some similar neurology.13,14 They also share reactions to toxins that have invaded the CNS. If the toxic load in a person is potent enough, the excitatory effects of the toxic material can cause similarly unbridled overstimulation, which we may recognize as chronic anxiety. Studies have shown the toxic effects on neurons by exposure to metal nanoparticles as an example.4 Toxins can significantly impact endocrine glands and can cause hormone imbalance, such as adrenal burnout, and elevated cortisol levels.
Toxins can significantly impact endocrine glands and can cause hormone imbalance, such as adrenal burnout, and elevated cortisol levels. Clinicians and researchers continue to search for more clarity on why benzodiazepine withdrawal is so difficult. Coming off these drugs is disruptive to the entire CNS and affects the amazingly complex relationships between neural connections, glands, muscles, etc., throughout the entire body.
Clinicians and researchers continue to search for more clarity on why benzodiazepine withdrawal is so difficult. Coming off these drugs is disruptive to the entire CNS and affects the amazingly complex relationships between neural connections, glands, muscles, etc., throughout the entire body. After as little as two to four weeks, tolerance can begin to develop. After tolerance develops, there is a decrease in the effectiveness of repeated doses of the medication.32 Tolerance occurs when the body begins to adapt to the presence of the drug. After establishing a degree of tolerance, stopping or reducing the drug can be expected to produce withdrawal symptoms.
After as little as two to four weeks, tolerance can begin to develop. After tolerance develops, there is a decrease in the effectiveness of repeated doses of the medication.32 Tolerance occurs when the body begins to adapt to the presence of the drug. After establishing a degree of tolerance, stopping or reducing the drug can be expected to produce withdrawal symptoms. When a person begins taking benzodiazepines for anxiety, for example, there will likely be an immediate relief for a period of time. However, when the drug is discontinued or reduced, the anxiety can “rebound,” or reappear, often more intensely than was experienced before the prescription began.8
When a person begins taking benzodiazepines for anxiety, for example, there will likely be an immediate relief for a period of time. However, when the drug is discontinued or reduced, the anxiety can “rebound,” or reappear, often more intensely than was experienced before the prescription began.8
 Benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome is a medical term that covers the effects of stopping benzo drugs. These physiological symptoms typically present in “waves” or phases, starting with the acute or immediate effects, which can include the rebound symptoms as discussed in the previous section.
Benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome is a medical term that covers the effects of stopping benzo drugs. These physiological symptoms typically present in “waves” or phases, starting with the acute or immediate effects, which can include the rebound symptoms as discussed in the previous section.
 Our clients have often gone to their prescribing physician and asked for help, but no help was available beyond switching medications, and sometimes even upping the dosage to “relieve” (mask) symptoms.
Our clients have often gone to their prescribing physician and asked for help, but no help was available beyond switching medications, and sometimes even upping the dosage to “relieve” (mask) symptoms.
 To summarize, the benzodiazepine taper program will begin with lab testing, to discover what corrective actions we can use to begin to normalize neurochemistry. There may be toxins, there may be deficiencies, and there may be genetic factors that show up that can be eased with properly targeted supplements or other protocols. Hormone or other imbalances, allergies, blood sugar levels, all play a part in designing the program for a successful and comfortable benzo taper.
To summarize, the benzodiazepine taper program will begin with lab testing, to discover what corrective actions we can use to begin to normalize neurochemistry. There may be toxins, there may be deficiencies, and there may be genetic factors that show up that can be eased with properly targeted supplements or other protocols. Hormone or other imbalances, allergies, blood sugar levels, all play a part in designing the program for a successful and comfortable benzo taper. Often, medical doctors who prescribe benzodiazepines do not have the training or experience to help their patients to withdraw from them. In fact, some physicians may express disbelief or lack of true comprehension of the difficulties that you are facing. They simply lack the training and that is why they could not have helped you, even if they desperately desired to do so.
Often, medical doctors who prescribe benzodiazepines do not have the training or experience to help their patients to withdraw from them. In fact, some physicians may express disbelief or lack of true comprehension of the difficulties that you are facing. They simply lack the training and that is why they could not have helped you, even if they desperately desired to do so.







